Air circulation in the same environments determines increase of CO₂ carbon dioxide and pollutants … to solve this problem we must renew it, taking fresh air renewal from the outside, heat it or cool it according to the season, and enter it into the environment.
The treatment of the air (hot or cold) involves an important energy cost, which can be greatly content recovering most of the part of the energycontained in the air stream output and transfer it to the renewal.
The heat recovery devices used in mechanical ventilation are air-air exchangers that allow the transfer of heat (and humidity in enthalpic version) between a flow of exhaust air and a return air flow (fresh, filtered). The heat exchanger, fans and the filters are positioned in an insulated casing with flanges for fitting to the channels, control / setting devices and devices pre- or post-treatment.
The operating point of a heat recovery unit is defined by the air flow rate (m³ / h) and the static pressure (Pa); recovery can be cross-flow, with a yield between 40 and 70%, or in countercurrent with yields higher than 80%, clearly with a higher cost. Heat -exchangers can recover the sensible heat (temperature) and also the latent heat (humidity).
The heat recovery units can be static or rotating; in the rotating heat exchanger speed is variable and adjustable to modulate the heat capacity. The fresh air and the expulsion cross each one half of the exchanger, in countercurrent: the air expelled cross one half of the cylinder and releases heat to the rotor, which accumulates it, the renewal air, which flows through the other half, absorbs heat previously accumulated. The cylinder slowly continuously rotates.
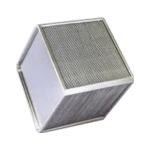
cross-flow in Al

counter-flow in Al

counter-flow in PP

rotating in AI